Our Space History
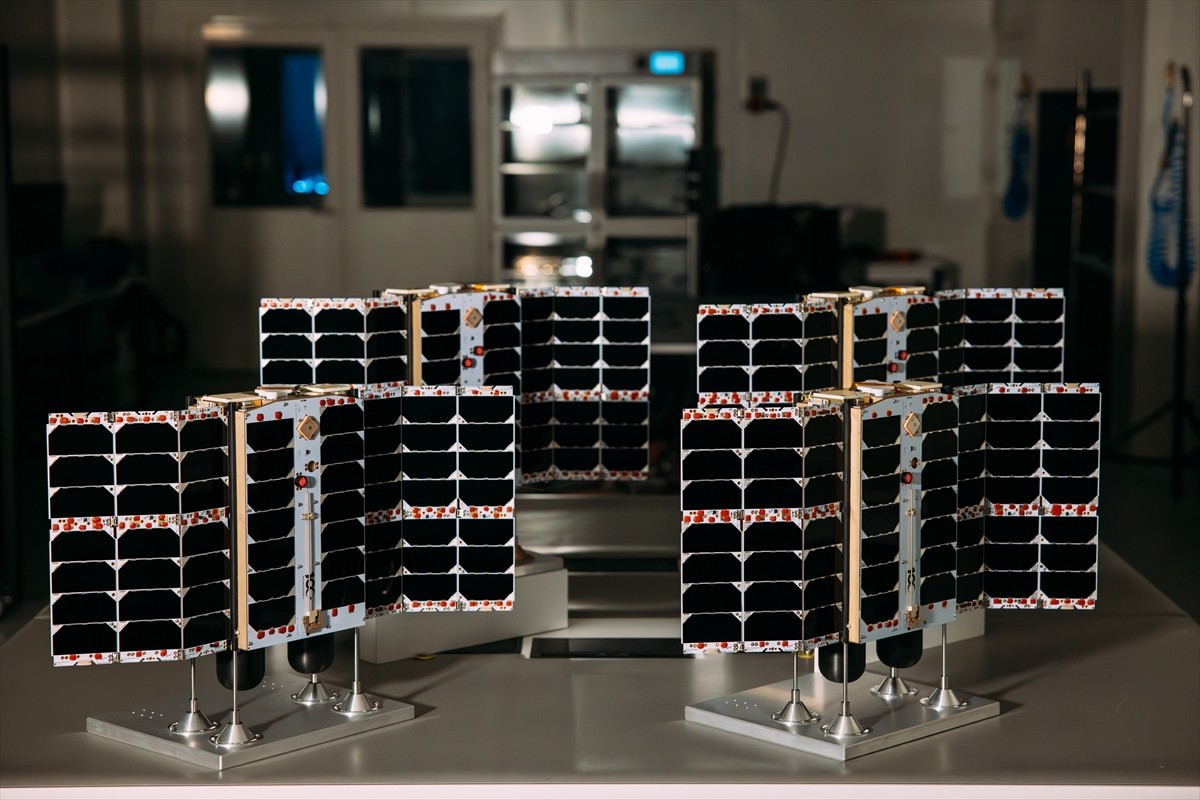

Plan S's 4 IoT satellites launched into space.

Istanbul University Institute of Astronomy was founded.
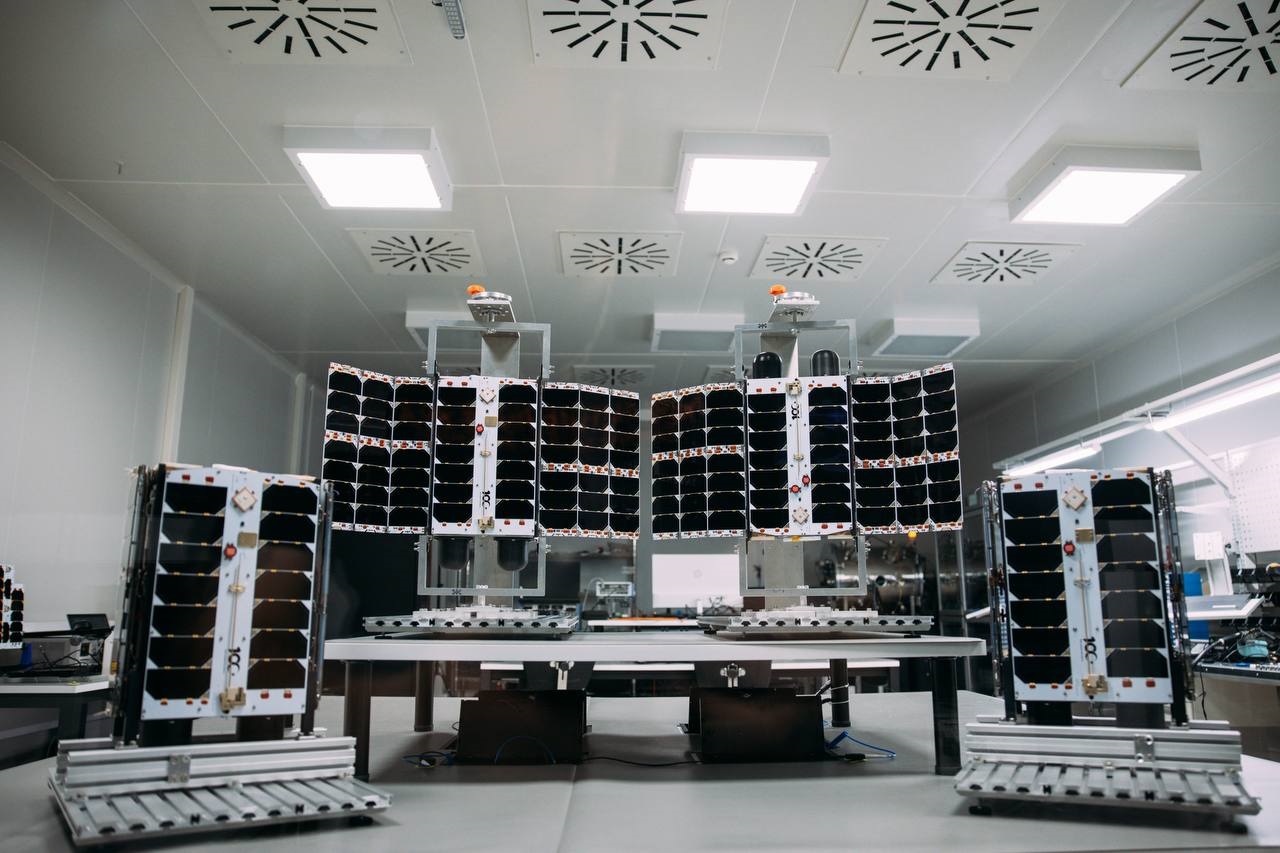

Plan S's 4 IoT satellites launched into space.
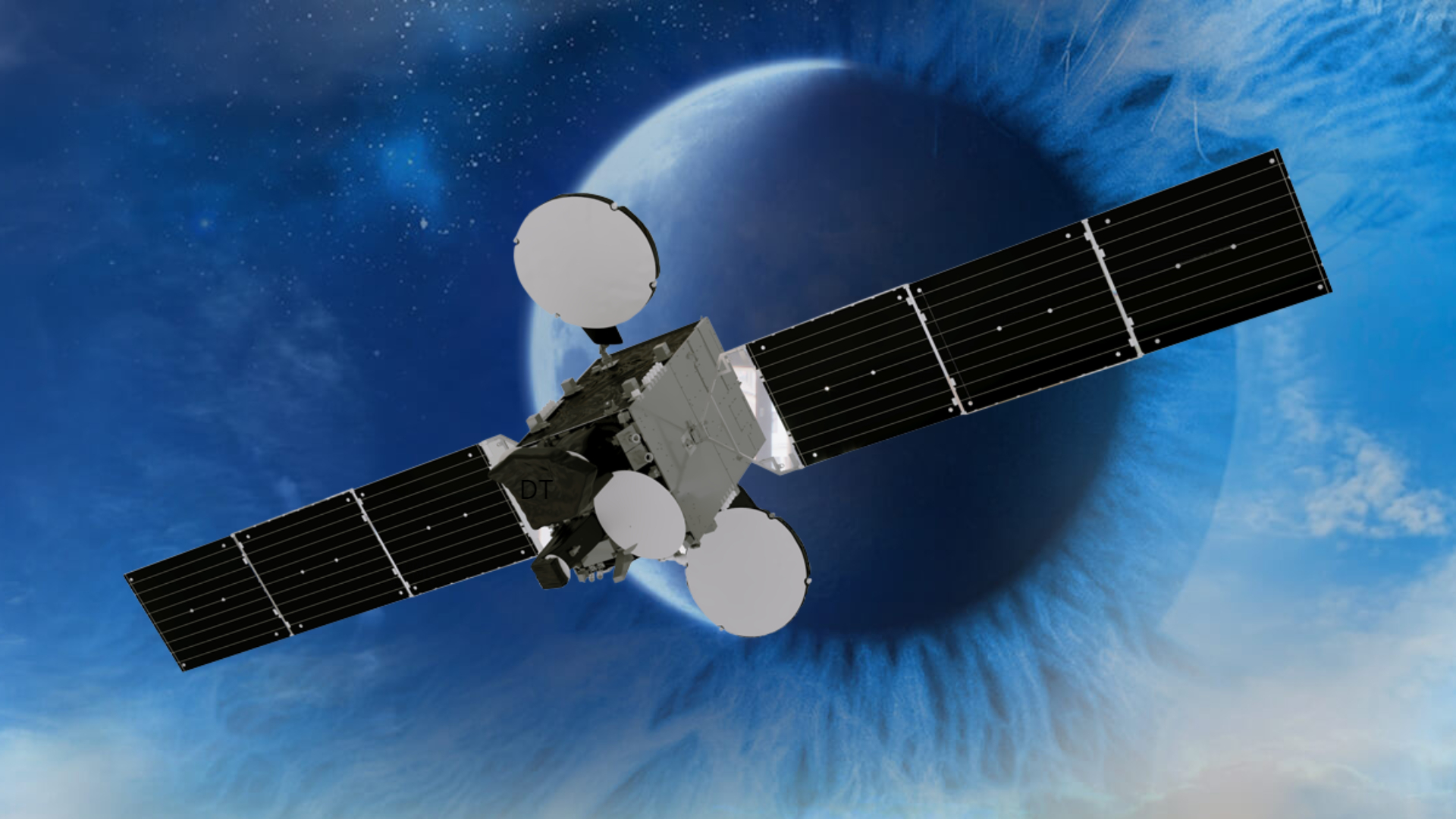

Our first domestic and national communications satellite TÜRKSAT 6A was launched.
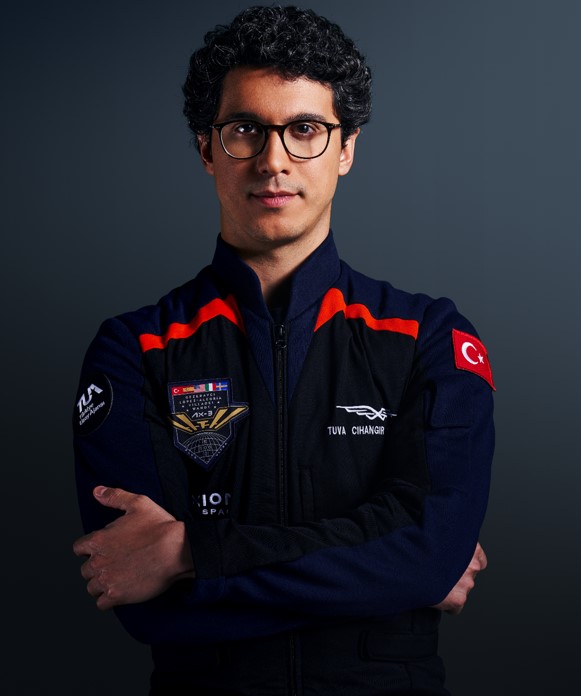

The second Turkish astronaut Tuva Cihangir ATASEVER carried out the Suborbital Research Flight as Turkish Space Science Mission,
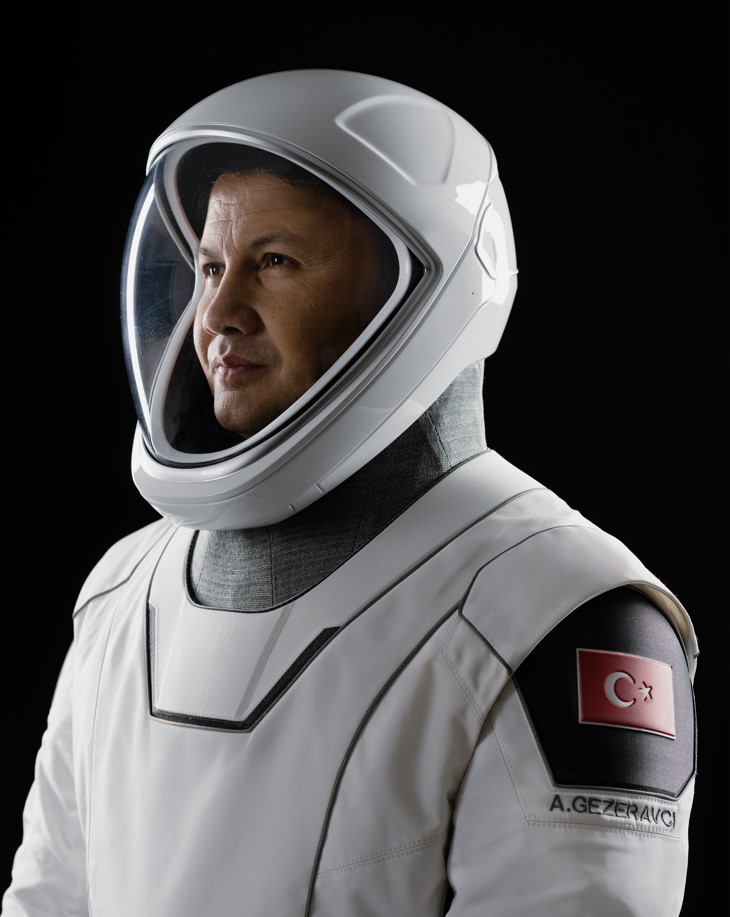

Alper GEZERAVCI, the first Turkish astronaut, traveled to the International Space Station as part of the Turkish Space Science Mission.
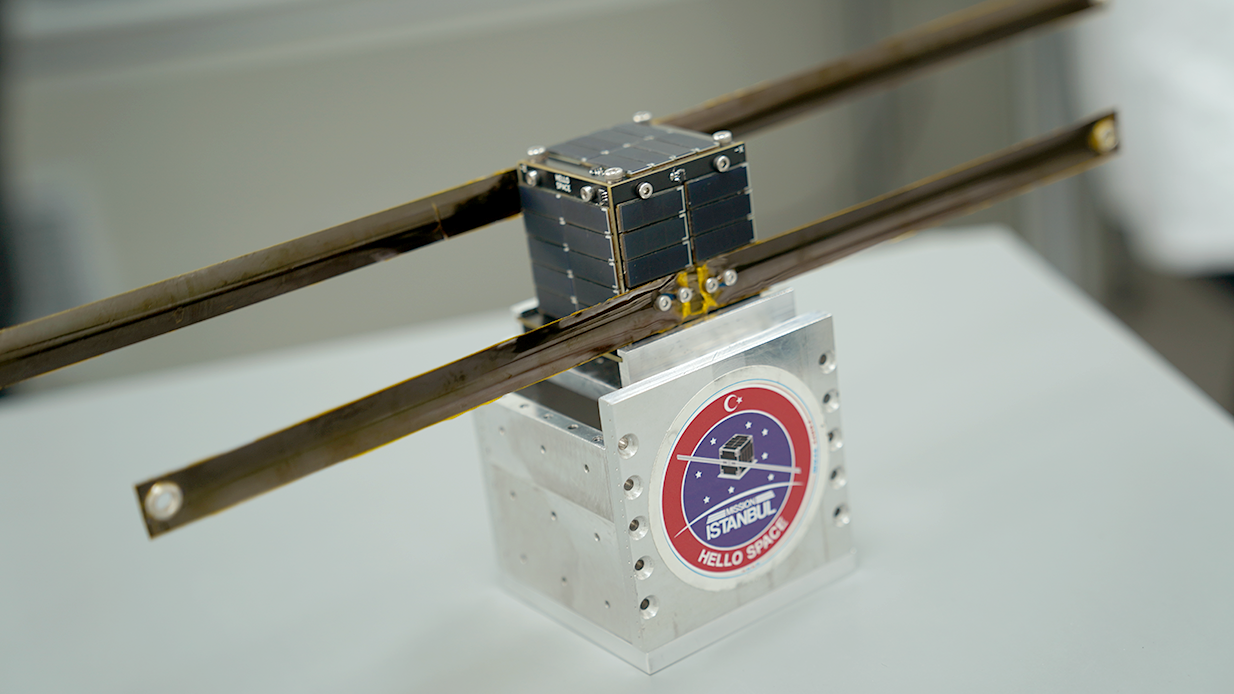
Hello Space's Istanbul Pocket Satellite was launched.

Plan S Connecta T3.1 and T3.2 were launched.
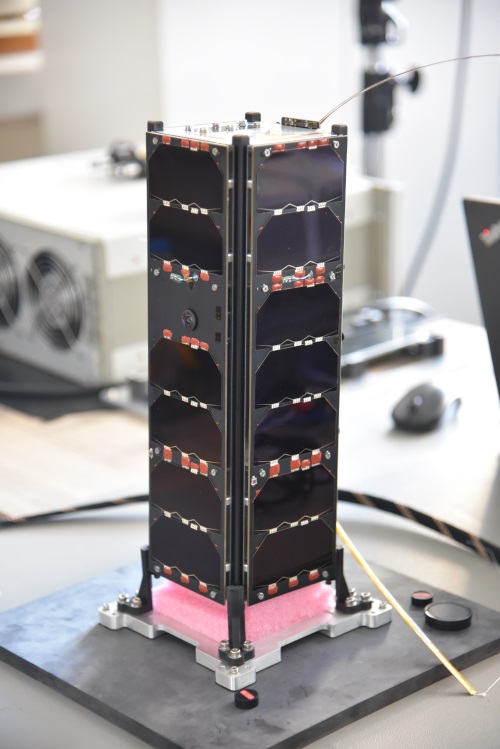
AKUP SSS-2B, a cube satellite developed under the APSCO project, was launched.
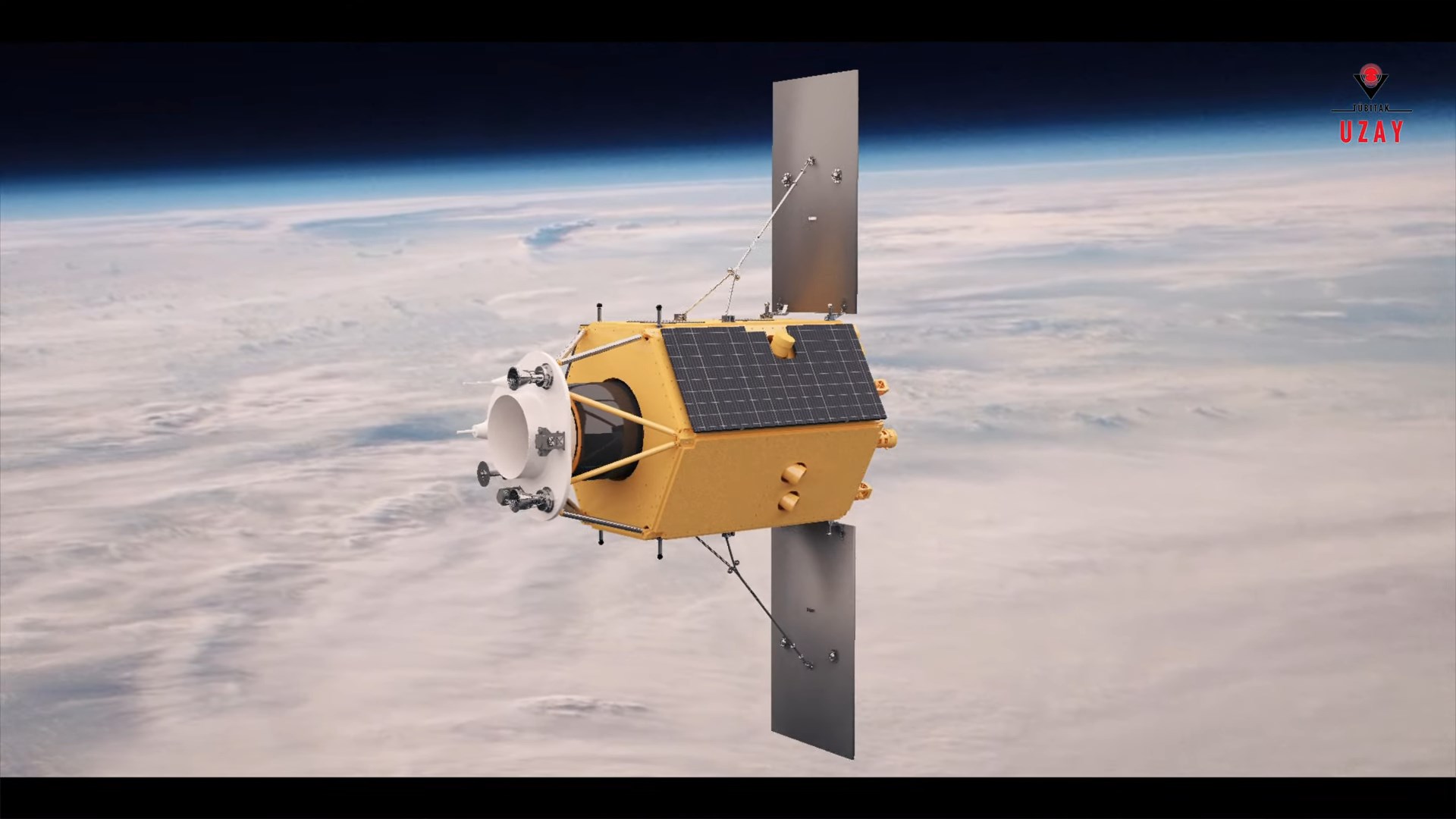

İMECE, our first domestic and national high-resolution imaging satellite, was launched.
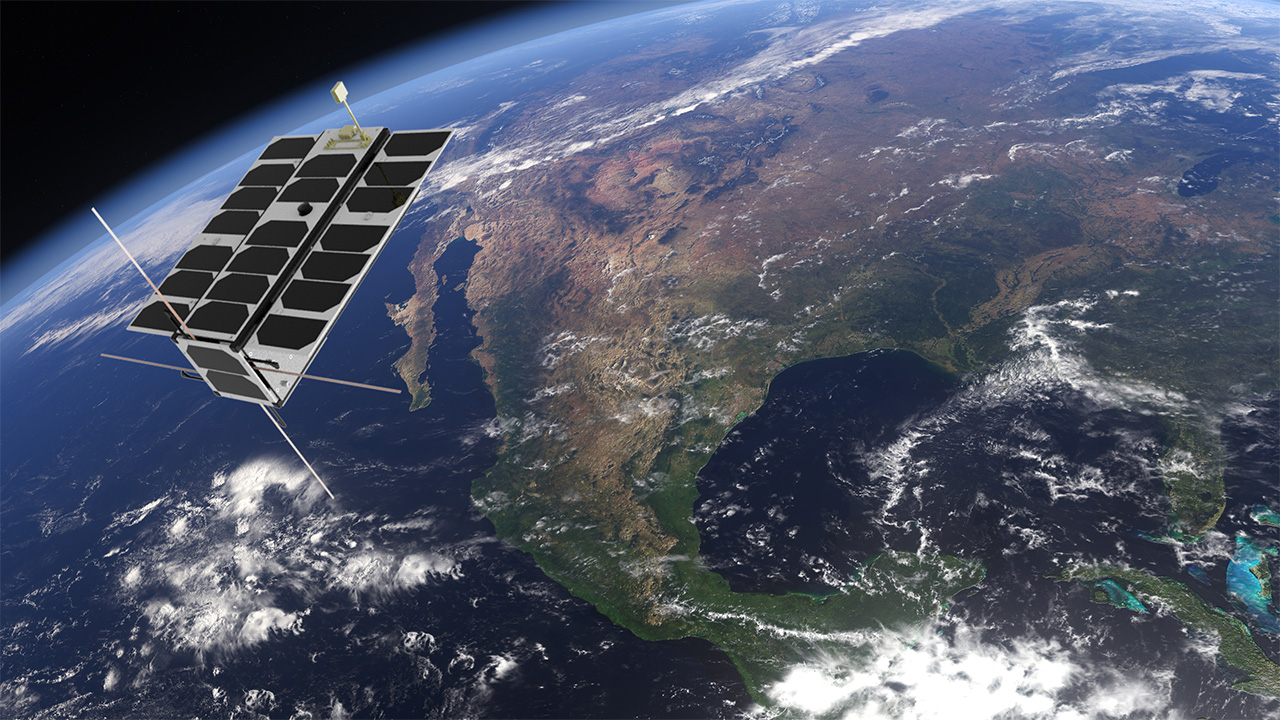

Plan S Connecta T1.2 and Connecta T2.1 were launched.
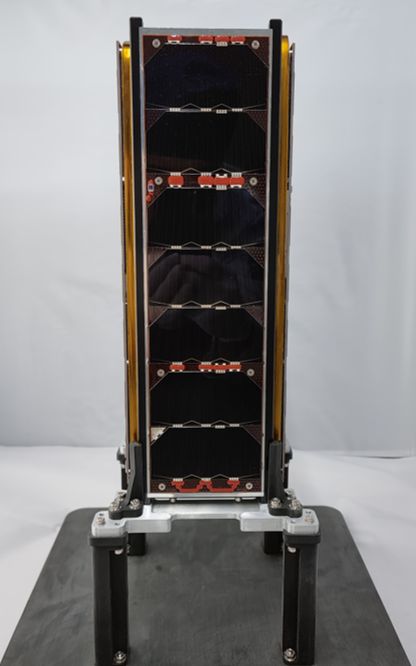

The KILIÇSAT cube satellite, which will be used in the defense industry, was launched.
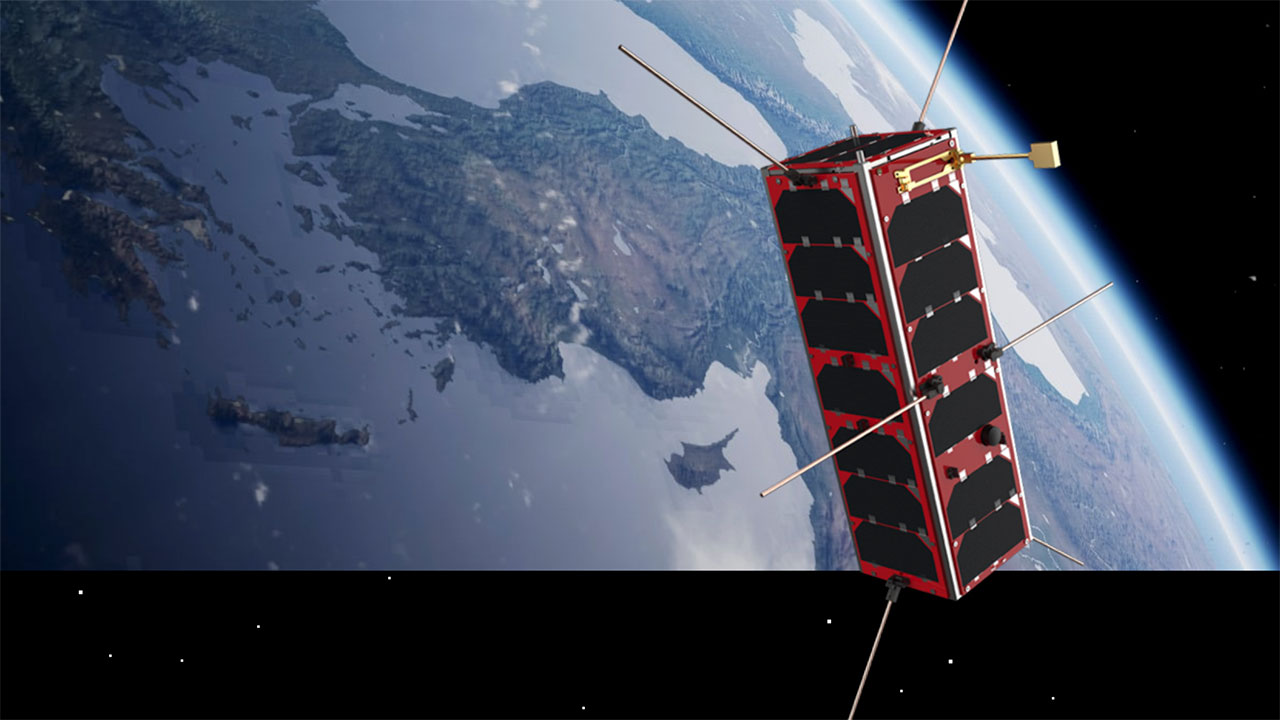

The first commercial satellite Plan S Connecta t1.1. was launched.
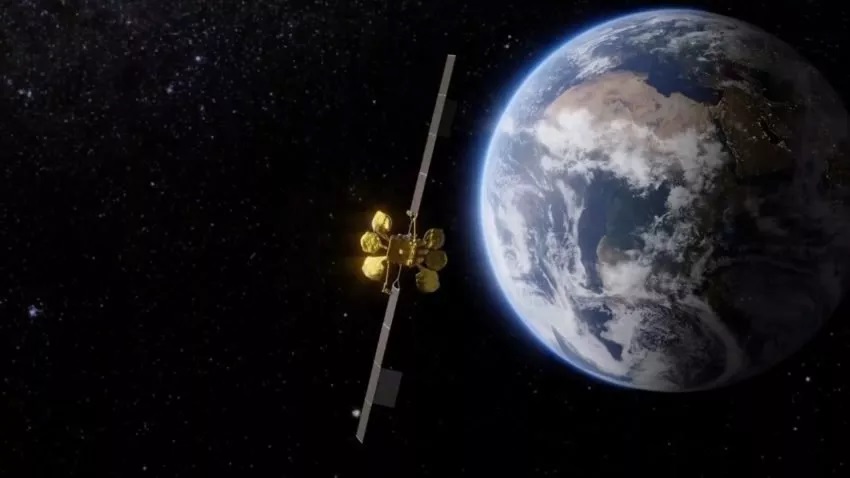

TÜRKSAT 5B was launched.

ASELSAT 3U was launched to the Low-earth Orbit (LEO).

TURKSAT 5A was inserted into the geostationary orbit at a longitude of 31 degree East.

Turkish Space Agency was established with the Presidential Decree Nr. 23.

UBAKUSAT was inserted to the Low-earth Orbit (LEO) from the ISS. It is in passive state today.

HAVELSAT was inserted to the Low-earth Orbit (LEO) from the ISS.It reentered to the atmosphere.

BeEagleSat was inserted to the Low-earth Orbit (LEO) from the ISS.It reentered to the atmosphere.

Fergani Space's first satellite FGN-100-d1 launched into space.

Göktürk-1, a high-resolution optical remote sensing satellite of Turkey, was launched. It is still active today.

TURKSAT 4B was inserted into the geostationary orbit at longitude of 50 degree East. It is still active today.

Turkish Space Systems, Integration and Test Center (USET) was founded.

TURKSAT 4A was inserted into the geostationary orbit at longitude of 42 degree East. It is still active today.

TÜRKSAT-3USAT was inserted to the Low-earth Orbit (LEO). It is in passive state today.

Göktürk-2, an indigenous high-resolution remote sensing satellite of Turkey, was launched.

RASAT, the second indigenous remote sensing satellite of Turkey, was launched.

İTÜpSAT1 was launched to operate as the first CubeSat of Turkey in the Low-earth Orbit (LEO).It is still active today.

TURKSAT 3A was inserted into the geostationary orbit at longitude of 42 degree East. It is still active today.

Turkey became a member of The Asia-Pacific Space Cooperation Organization (APSCO).

BILSAT, the first experimental remote sensing satellite of Turkey, was launched. It is in passive state today.

TURKSAT 2A was inserted into the geostationary orbit at longitude of 31 degree East. It is in passive state today.

TUBITAK National Observatory was inaugurated. It hosts various optical telescopes largest of which has a radius of 1.5 m.

TURKSAT 1C was inserted into the geostationary orbit at longitude of 31 degree East. It is in passive state today.

TURKSAT 1B was inserted into the geostationary orbit at longitude of 31 degree East. It became the first telecommunication satellite of Türkiye. It is in passive state today.

Turkey became a founding member of European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT).

Istanbul Technical University Faculty of Aeronautics and Astronautics was founded.

Our first national ground station AKA-1 (Ankara 1) entered into service upon the installment of 11 telephone channels with the United Kingdom of Great Britain.

The United Nations Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies is signed by Türkiye.

The components that are planned to be used in the development of indigenous satellite technologies were launched. The space environment tests of these components will be conducted in the Japanese KIBO Module on the International Space Station (ISS).
